Sublimation and Heat Transfer are two well-liked techniques for producing excellent pictures on a variety of substrates, but they are not the same in a few important ways. We will examine the differences between these two methods in this blog article, illuminating their traits, uses, and benefits.
Sublimation Printing
How It Works: The method of sublimation printing transfers a pattern from sublimation paper to a substrate, such cloth, mugs, or metal, by using pressure and heat. The ability of dye-based ink to change from a solid to a gaseous state when heated is what distinguishes sublimation. After then, the ink fuses with the substance to form a vital component. The original color of the material is retained in the print, producing vivid, long-lasting pictures that don’t fade or fracture with time.

Color Compatibility: Because the ink blends into the substrate, sublimation printing works best on white or light-colored materials. This lets the material’s true color show through.
Durability: The robustness of sublimation prints is well-known. Because the ink is ingrained in the substance, it is extremely resilient to peeling, fading, and breaking.
Versatility: The materials and forms on which sublimation printing may be applied are a little restricted. For optimal results, the fabric must have a high percentage of polyester and a flat or slightly curved surface.
Heat Transfer
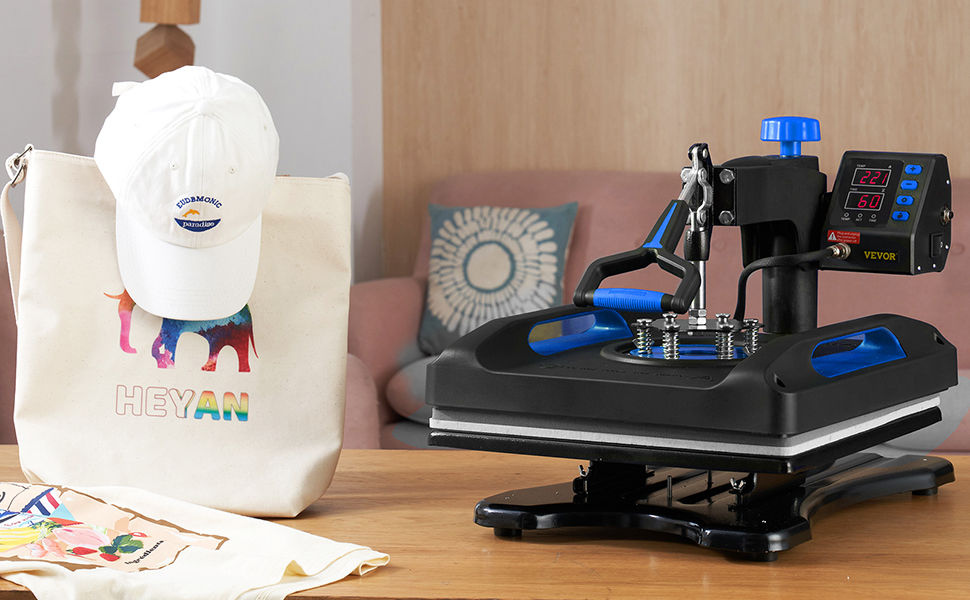
How It Works: When pressure and heat are applied to a material, ink is transferred to its surface to facilitate heat transfer printing. In contrast to sublimation, the ink creates a coating on top of the material instead of absorbing into it, resulting in a contrast with the original color of the material.
Color Compatibility: Since the ink lies on the surface and is not dependent on the color of the substrate, heat transfer may be applied to materials of any color.
Durability: Heat transfer prints are more prone to fading even though they may generate crisp, colourful images. Over time, the ink coating on the surface may be scraped or removed by washing.
Versatility: Heat transfer printing is more flexible in terms of material and shape. It only needs one heat press and transfer paper that can be used on different types of substrates.

Choosing Between Sublimation and Heat Transfer
It’s up to you to decide if you want to go with sublimation printing or heat transfer. Sublimation and Heat Transfer decision depends on what you need and what you have available. Here are some things to think about:
- Project Outcome: Sublimation printing is a superior option because it embeds the ink inside the material, if longevity is what you’re after. Heat transmission works better in situations when durability is not the main consideration or in short-term applications.
- Materials and Colors: Heat transfer may be used on substrates of any color, however sublimation printing works best on white or light-colored materials.
- Complexity: eat transfer works well for straightforward designs with few colors and solid forms, but sublimation printing is better suited for intricate patterns, gradients, and all-over prints.
- Environmental Impact: Compared to screen printing, which requires water and chemicals for cleanup, sublimation printing is thought to be more ecologically friendly since it produces no waste or uses less water.
- Quantity: Because sublimation printing requires less setup, it is more affordable for small batches or one-off prints, whereas heat transfer becomes more cost-effective for greater numbers.
- On-Demand Fulfillment: Because sublimation printing makes personalization rapid and simple, it’s a great fit for on-demand fulfilment. Due to setup complexity, heat transmission is less flexible in on-demand settings.

By taking these factors into account, you can select the method that best fits your project’s needs and limitations. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, and understanding these differences will help you make the best choice.
So, there you have it. Sublimation vs Heat Transfer. Both methods are versatile and can be used for a variety of purposes. The best way to choose one or the other depends on your goals and the resources available to you.
If you would like more information about each method, check out the additional resources below.
Additional Resources:
- Mastering Sublimation Printing: Common Mistakes to Avoid – Discover how to avoid common mistakes in sublimation printing for flawless results.
- Cost Difference between Sublimation and Heat Transfer – Explore the cost differences between sublimation and heat transfer printing methods for various project scales.
- Difference between Sublimation and Screen Printing – Learn about the distinctions between sublimation and screen printing for transferring designs onto fabrics and materials.
FAQs
Q1: What is Sublimation Printing and how is it different from Heat Transfer Printing?
Ans: Sublimation printing works by heating and pressing down on the ink to turn it into a gas that bonds to the material. This creates vibrant, long-lasting prints. On the other end of the spectrum, heat transfer printing uses heat to apply ink to the material to create a layer that contrasts with it.
Q2: Which is better for printing dark-colored material, Sublimation or Heat Transfer?
Ans: Heat transfer printing is better for dark color materials because it creates a color layer on the surface that matches the color of the substrate. It works best on either white or light color materials.
Q3: Are Sublimation Prints More Durable than Heat Transfer Prints?
Ans: Yes, Sublimation and Heat Transfer Prints are both more durable than Heat Transfer Printing. The ink bonded to the material becomes a part of it, so it won’t fade, crack, or peel.
Q4. Can I use sublimation and heat transfer on a wide range of materials?
Ans: Sublimation printing is limited to materials with a high polyester content and flat or slightly curved surfaces. Heat transfer printing offers greater versatility and can be applied to a wider range of substrates.
Q5. Which method is more cost-effective for small-scale or one-off printing projects?
Ans: Sublimation printing is more cost-effective for small-scale or one-off projects, as it requires minimal setup and offers lower per-unit printing costs.
Q6. Which method is better for complex and detailed designs with multiple colors?
Ans: Sublimation printing is better suited for complex and detailed designs with multiple colors, gradients, and all-over prints. Heat transfer is ideal for simpler designs with fewer colors.
Q7. Is one method more environmentally friendly than the other?
Ans: Sublimation printing is considered more environmentally friendly as it doesn’t use water or generate waste. Heat transfer may involve the use of water and chemicals for cleanup, potentially leading to excess ink and paper waste.





One Comment on “Difference between Sublimation and Heat Transfer”